Project Phoenix: DNA unlocks a new understanding of coral
by Melissa Lyne 19 Sep 2020 22:03 UTC
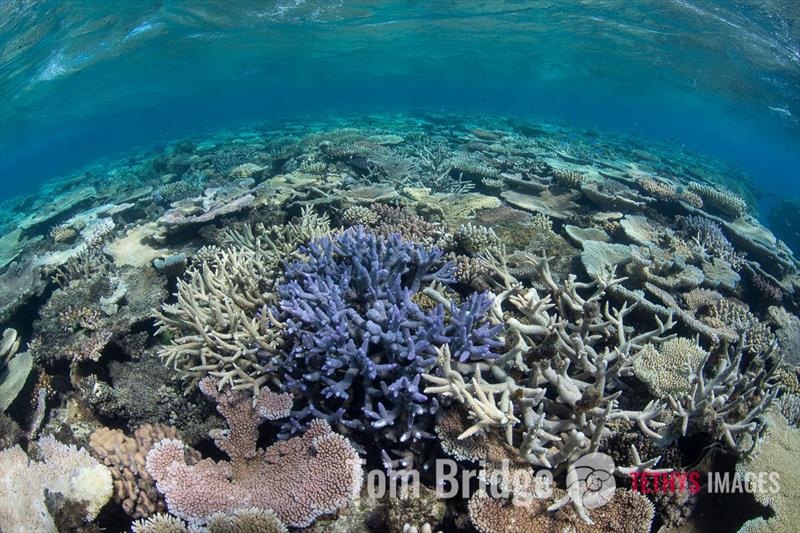

Scientists can't identify many coral species accurately—even in well-researched locations © Tom Bridge
Scientists have developed a new genetic tool that can help them better understand and ultimately work to save coral reefs.
"Surprisingly, we still don't know how many coral species live on the Great Barrier Reef, how to identify them, or which species live where. And those are the first steps in saving an ecosystem like that," said Dr Peter Cowman from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies at James Cook University (Coral CoE at JCU).
Dr Cowman led an international study on coral classification. Classification explains how species are related to each other. Shared similarities and differences provide a key to help identify species. For example, dogs and cats are classified on different branches of the evolutionary tree using their body design.
A seemingly finer detail, like how cats can retract their claws and dogs cannot, helps people decide whether a newly discovered species of small carnivore is more like a dog or a cat.
Dr Cowman said an important challenge when identifying corals is that the same species can grow in many different ways.
"For instance, some species can grow with either a plate or branch structure. The study found classifying corals by their physical characteristics didn't match the classifications based on their genetics," he said.
Species identification underpins almost all biological and ecological research, and the new study challenges more than 200 years of coral classification. The researchers say the 'traditional' method does not accurately capture the differences between species or their evolutionary relationships.
Co-author Professor Andrew Baird, also from Coral CoE at JCU, led a recent scientific journey along the Great Barrier Reef, uncovering 'treasure troves' of new, unidentified coral species.
"The traditional classification of corals is dead," Prof Baird said.
"But these new molecular tools allow us to reinvent a new classification system on the ashes of the old. Hence, the name we have given to the research: Project Phoenix," he said.
"These are exciting times to be a coral taxonomist."
"We need to review the way we currently identify corals," said co-author Dr Tom Bridge from Coral CoE at JCU, who is also the curator of corals at the Queensland Museum.
Dr Bridge said research in the past ten to 20 years has already revolutionised the understanding of the older branches on the evolutionary tree of corals. But, to date, there has been little progress on the more recent twigs of the 'tree'—the living species—particularly with the most diverse and ecologically-important group: the Acropora.
"The Acropora are the branching 'staghorn' corals that dominate reefs," Dr Bridge said. "Yet, even in well-researched locations like the Great Barrier Reef, we can't identify many of these species accurately."
Dr Cowman said the traditional method doesn't reflect the tens of millions of years of coral evolution.
"At the moment, we're flying blind," he said.
Dr Andrea Quattrini, curator of corals at the Smithsonian Institution's National Museum of Natural History, developed the new genetic tool. She said it provides a way forward with plans to secure the future of coral reefs.
"By comparing thousands of key genetic coral features, we were able to discern the evolutionary relationships of corals from the Great Barrier Reef and broader Indo-Pacific region," Dr Quattrini said.
"The result is a new classification that provides important scientific knowledge to assess the various intervention strategies currently being proposed on the Great Barrier Reef and elsewhere."
Some of the interventions being proposed on the reef include hybridising species and moving some populations south.
"It's clear we do not know enough about many of the species we're dealing with. This new method can help generate the robust science we need to assess such proposals," Dr Bridge said.
Paper
Cowman P, Quattrini A, Bridge T, Watkins-Colwell G, Fadli N, Grinblat M, Roberts E, McFadden C, Miller D, Baird A. (2020). 'An enhanced target-enrichment bait set for Hexacorallia provides phylogenomic resolution of the staghorn corals (Acroporidae) and close relatives'. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. DOI: 10.1016/j.ympev.2020.106944.